The Most Adaptable Animals in the Harshest Environments
The natural world is teeming with life forms that have evolved to thrive in diverse and often extreme environments. From scorching deserts to the icy tundra, these animals exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive and even flourish in conditions that would be fatal to most other species. Here, we explore some of the most adaptable animals that have mastered the art of survival in the harshest environments on Earth.
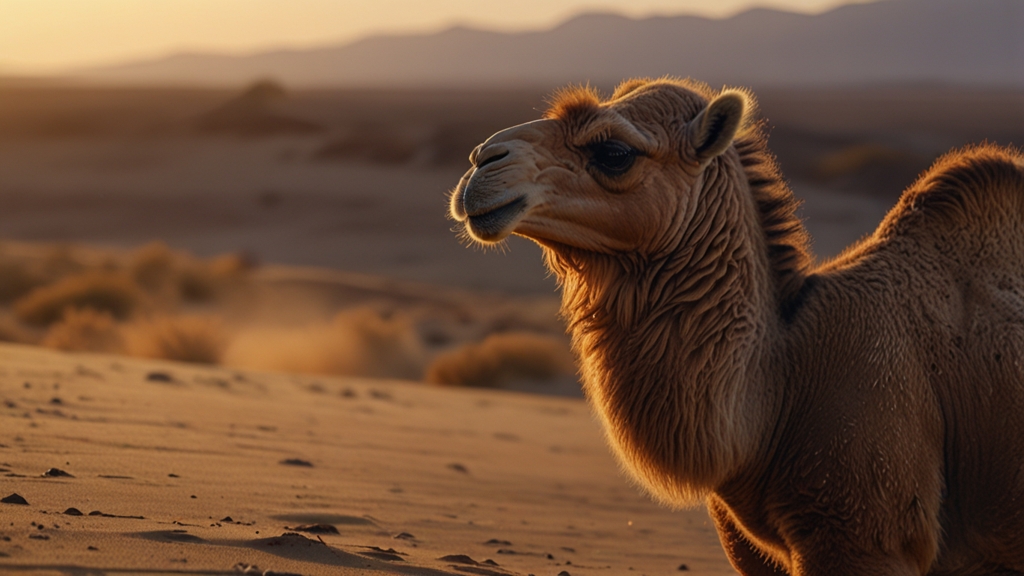
Desert Survivors: Camels
Camels are often cited as the quintessential desert survivors. These "ships of the desert" possess numerous adaptations that make them uniquely suited to arid climates. Their humps, contrary to popular belief, store fat, not water. This allows them to endure long periods without food. Camels can also drink up to 40 gallons of water in one go, replenishing their hydration levels rapidly.
Camels have evolved to cope with extreme heat. They can withstand body temperatures of up to 104 degrees Fahrenheit before sweating, which helps conserve precious water.
Their nostrils can close to keep out sand, and they have thick eyebrows and long eyelashes to protect their eyes from the harsh sun and blowing desert sands. These physical adaptations, combined with their behavioral traits such as traveling in groups to reduce exposure to predators, make camels true desert dwellers.
Antarctic Adaptations: Emperor Penguins
No list of adaptable animals would be complete without mentioning the emperor penguins of Antarctica. These resilient birds endure some of the coldest temperatures on the planet, where average winter temperatures hover around -40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Emperor penguins have a layer of fat that insulates them from the cold, and their feathers are densely packed, providing additional thermal protection. During the breeding season, males huddle together in large groups to conserve warmth, often standing for weeks without food while incubating their eggs.
The social behavior of huddling not only conserves heat but also allows penguins to rotate positions, ensuring that no individual spends too long on the periphery, exposed to the biting cold.
These adaptations enable emperor penguins to not only survive but also raise their young in one of the most inhospitable places on Earth.
Deep Sea Dwellers: Anglerfish
The deep sea is another extreme environment where only the hardiest creatures can survive. Among the most fascinating of these is the anglerfish. Living at depths where sunlight never penetrates, anglerfish have evolved unique adaptations to navigate and hunt in complete darkness.
The most distinctive feature of the anglerfish is its bioluminescent lure, a modified dorsal spine that protrudes above its mouth, glowing to attract prey. This "fishing rod" technique is an ingenious adaptation to an environment where food is scarce.
Anglerfish exhibit extreme sexual dimorphism. Males are tiny compared to females and have evolved to latch onto a female's body, eventually fusing and sharing a blood supply. This ensures reproductive success in the sparsely populated deep sea.
Their huge mouths and expandable stomachs allow them to consume prey of a substantial size, a crucial adaptation in an environment where meals are few and far between.
Survival in High Altitudes: Himalayan Snow Leopard
High-altitude regions present a unique set of challenges, including low oxygen levels, frigid temperatures, and rugged terrain. The Himalayan snow leopard is a master of this environment. These elusive felines are built for life in the mountains. Their broad paws function like natural snowshoes, allowing them to traverse snowy landscapes with ease.
Snow leopards have thick fur that provides insulation against the cold, and their long, bushy tails serve as additional warmth when wrapped around their bodies. They also have a well-developed chest and lung capacity to efficiently process the thin mountain air, an essential adaptation for high-altitude living.
Their keen eyesight and exceptional camouflage help them hunt in rocky terrains where prey can be scarce, making them proficient and patient predators.
Conclusion
From deserts to polar ice caps, deep seas to high mountains, animals have developed an incredible array of adaptations to thrive in the harshest environments Earth has to offer. These evolutionary marvels remind us of the resilience and ingenuity of life, capable of overcoming seemingly insurmountable challenges to survive and prosper.