Animal Adaptations: How They Survive in Extreme Conditions
Throughout the natural world, animals have evolved a fascinating array of adaptations that allow them to survive in some of the most extreme environments on Earth. From the icy realms of the Arctic to the blistering sands of the Sahara, these remarkable adaptations showcase the resilience and ingenuity of the animal kingdom.
Surviving the Cold
The Arctic and Antarctic regions are some of the most inhospitable places on the planet. Temperatures can plummet far below freezing, and the landscape is often covered in snow and ice. Yet, a diverse array of animals thrives in these frigid environments. Polar bears, for instance, have evolved a thick layer of blubber and dense fur to insulate against the cold, while their black skin absorbs heat from the sun.
“Nature never ceases to amaze with the sheer adaptability of life. Animals in the polar regions are prime examples of evolutionary success stories.”
Similarly, the Arctic fox has developed a compact body size and short limbs to minimize heat loss, along with a coat that changes color with the seasons – white in winter to blend in with the snow, and brown in summer for the tundra.
Enduring the Heat
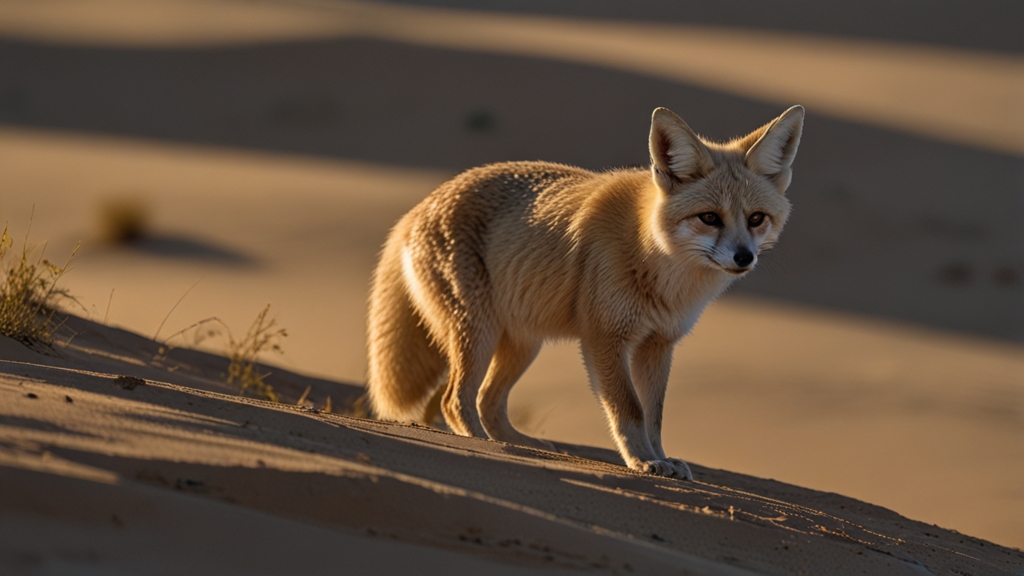
At the other extreme, desert environments present their own set of challenges. Scorching temperatures, scarce water, and limited shelter require specialized adaptations for survival. The fennec fox, native to the Sahara Desert, is equipped with large ears that dissipate excess heat and allow them to hear predators from a distance. Their kidneys are adapted to excrete highly concentrated urine to conserve water.
Similarly, camels have become synonymous with desert survival. These “ships of the desert” can endure long periods without water, thanks to their ability to store fat in their humps. When water does become available, camels can drink up to 40 gallons in one go, replenishing their reserves until the next opportunity.
“The extreme adaptability of desert animals, such as the camel, is a testament to nature's ingenious solutions for survival under harsh conditions.”
Thriving Underwater
The deep ocean is another extreme environment, characterized by high pressure, low temperatures, and total darkness. Deep-sea creatures have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in these conditions. The anglerfish, for example, uses a bioluminescent lure to attract prey in the pitch-black depths. Their massive, sharp teeth ensure nothing escapes once caught.
Similarly, the giant tube worms found near hydrothermal vents have a symbiotic relationship with chemosynthetic bacteria, which convert the toxic chemicals emitted by the vents into nutrients for the worms. Such adaptations allow life to flourish even in the most unexpected places.
The High Life
High-altitude environments present a combination of low oxygen levels, frigid temperatures, and intense UV radiation. Yet, animals like the llama and yak are perfectly adapted to these conditions. Llamas have a higher concentration of red blood cells, enabling them to efficiently transport oxygen throughout their bodies in low-oxygen environments. Yaks, on the other hand, possess a thick woolly coat to protect against the cold and have large lungs for increased oxygen uptake.
“Adaptations of high-altitude animals, such as the llama, underscore the remarkable capabilities of evolution in catering to life's needs even at the roof of the world.”
Another high-altitude dweller, the Himalayan snow leopard, has powerful limbs for scaling steep cliffs and a long tail for maintaining balance. Their thick fur and large nasal cavities warm the cold air before it reaches their lungs.
Conclusion
Animal adaptations to extreme conditions highlight the remarkable versatility and resilience of life on Earth. These adaptations are not only testament to the power of evolution but also showcase the incredible diversity of strategies that animals use to thrive in some of the harshest environments known to man. Understanding these adaptations not only enriches our appreciation of the natural world but may also offer insights into how life can survive in seemingly uninhabitable places, potentially even beyond our planet.