The Unspoken Rules of Animal Hierarchies Revealed
At first glance, the animal kingdom might seem like a chaotic and unpredictable place. However, beneath the surface lies a complex system of social structures and hierarchies that govern the lives of various species. These unspoken rules of animal hierarchies determine everything from mating rights to access to resources. Understanding these intricate social constructs can provide profound insights into the behavior and survival strategies of animals.
Dominance and Submission
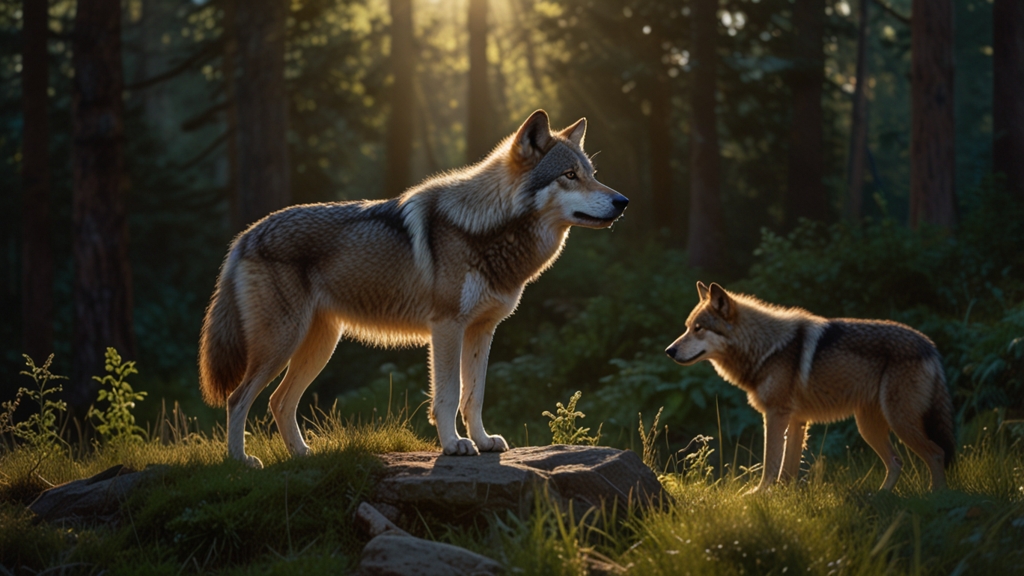
In many animal societies, dominance hierarchies are established to reduce conflict and ensure that resources are distributed efficiently. A dominant individual, often referred to as the "alpha," typically enjoys priority access to food, shelter, and mates. Subordinate animals, on the other hand, may have to wait their turn or settle for less desirable resources.
In a pack of wolves, the alpha pair leads the group, making decisions about hunting and territory defense. The social order is reinforced through displays of dominance and submission, such as body posture, facial expressions, and vocalizations.
These displays serve to minimize physical confrontations, as a well-established hierarchy reduces the need for constant battles. The alpha may also benefit the group by leading them to abundant food sources and protecting them from threats.
The Role of Alliances and Coalitions
While physical strength and aggression often play a role in establishing dominance, alliances and coalitions can be equally important. In species such as chimpanzees and dolphins, individuals form bonds with others to increase their social standing and influence.
Research has shown that male dolphins form coalitions to control access to females, while female dolphins form alliances to protect their offspring from aggressive males.
These alliances are not static; they can shift based on the current social landscape and the individuals involved. The ability to form and maintain alliances requires advanced cognitive skills and social intelligence, demonstrating the complexity of these animal societies.
Access to Mating Opportunities
In many species, social hierarchies directly impact reproductive success. The highest-ranking males and females are often the most successful in passing on their genes, either through direct control of mating opportunities or through more subtle means such as mate choice.
Among peafowls, for example, females preferentially mate with males that have the most extravagant tail feathers, a sign of good health and superior genetics. These males often occupy the top tiers of the social hierarchy.
Moreover, lower-ranking individuals may employ alternative reproductive strategies to circumvent their social limitations. This can include sneaky mating tactics, cooperative breeding, or even directly challenging higher-ranking individuals during opportune moments.
Resource Allocation and Survival
Hierarchy not only influences mating opportunities but also affects access to vital resources like food and shelter. In species where resources are scarce, dominant individuals can hoard these essential supplies, ensuring their own survival and the survival of their offspring.
For instance, in meerkat societies, the dominant female often controls breeding within the group, while subordinate females act as helpers to raise the dominant female's pups. This cooperation ensures that the genes of the most fit individuals are passed on, while minimizing wasteful competition over limited resources.
The Complexity of Social Signals
The unspoken rules of animal hierarchies are communicated through a rich tapestry of social signals. These include vocalizations, body language, scent marking, and even changes in coloration or physical appearance. Understanding these signals requires keen observation and a deep appreciation of the nuances within animal behavior.
For example, the intricate dance of honeybees is a form of communication that conveys information about food sources and the status of the hive. This dance not only helps organize the collective efforts of the hive but also reinforces the queen's status as the central figure in the colony.
Conclusion
The unspoken rules of animal hierarchies reveal a fascinating world of social complexity and cooperation. From dominance and submission to alliances and resource allocation, these hierarchies play a crucial role in the survival and reproduction of countless species. By studying these systems, researchers gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary pressures that shape behavior, ultimately shedding light on the intricate balance of life in the animal kingdom.