Lifeline to the Future: The Role of Endangered Species in Ecosystems
In the intricate web of life that constitutes our planet's ecosystems, every species plays a unique and vital role. However, the alarming rise in the number of endangered species poses a significant threat to these finely balanced systems. From the smallest insects to the largest mammals, the loss of any species can lead to unforeseen and often devastating consequences. Understanding the importance of endangered species is crucial for ensuring the health and stability of our natural world.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present in a given ecosystem. This diversity is essential for the resilience and functionality of ecosystems. Each species, whether it is a plant, animal, or microorganism, contributes to the ecosystem's overall health. They participate in numerous processes such as pollination, seed dispersal, nutrient cycling, and decomposition. The interactions among species create a network that maintains ecological balance.
Biodiversity is not just about the sheer number of species, but the variety of living organisms; the different plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. - David Attenborough
When a species becomes endangered, its reduced numbers can lead to diminished biodiversity. This weakens ecosystem resilience, making it more vulnerable to environmental stressors like climate change, natural disasters, and human activities.
Keystone Species and Their Impact
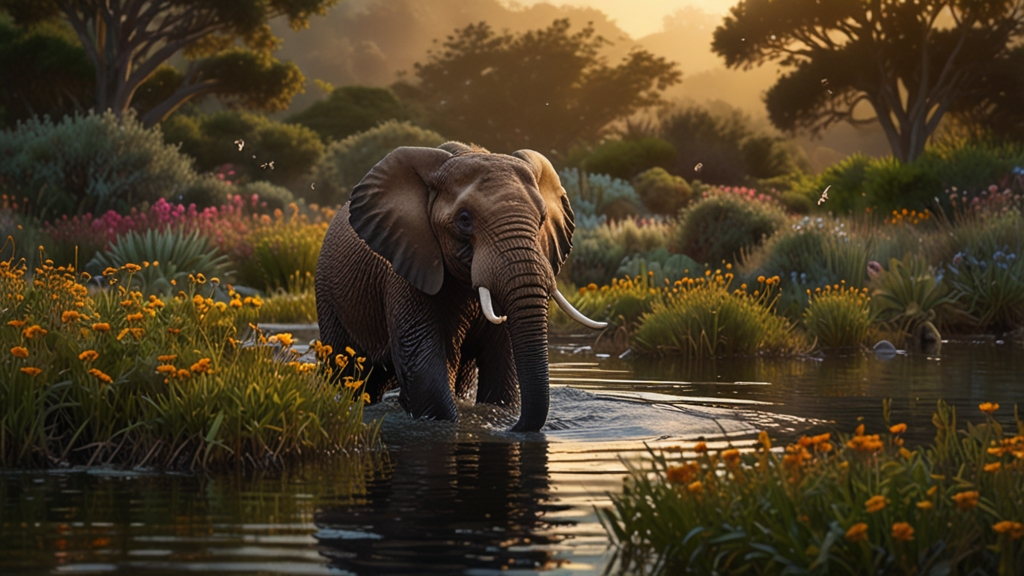
Some species have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystems. These are known as keystone species. The removal of a keystone species can lead to a domino effect, causing drastic changes in the ecosystem. For instance, the African elephant is a keystone species in the savanna ecosystem. By uprooting trees and shrubs, elephants create open spaces that facilitate the growth of grasses, which are crucial for other herbivores.
Another example is the sea otter, which preys on sea urchins. Without sea otters, sea urchin populations can explode, leading to the overgrazing of kelp forests. These forests are vital marine habitats that support a variety of marine life. Thus, the reduction or loss of keystone species can lead to habitat degradation and species collapse.
The Ripple Effect of Extinction
Extinction does not occur in isolation. The loss of one species can trigger a cascade of effects throughout the ecosystem. This phenomenon is often termed the "ripple effect." For example, the decline of pollinators like bees can affect plant reproduction, leading to reduced availability of fruits and seeds. This, in turn, impacts animals that rely on those plants for food.
The fate of endangered pollinators and the plants that they pollinate are profoundly intertwined. - Sandra M. Rehan
Predator-prey relationships are also significantly impacted. If a predator species becomes endangered or extinct, the prey population may grow unchecked, leading to overgrazing or depletion of vegetation. Conversely, the loss of a prey species can result in the decline of predator populations due to lack of food.
Conservation Efforts
The conservation of endangered species is not just about saving individual species, but about maintaining the balance of entire ecosystems. Conservation programs often focus on habitat protection, restoration, and the establishment of protected areas. Captive breeding and reintroduction programs are also implemented to bolster populations of critically endangered species.
Public awareness and education play pivotal roles in conservation efforts. By educating communities about the importance of endangered species and the role they play in ecosystems, we can foster a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards our natural world.
Conclusion
Endangered species are indeed the lifelines to the future health of our ecosystems. Their roles, whether visible or hidden, are integral to the stability and functionality of the environment. The loss of any species, especially keystone species, can have cascading effects that disrupt ecological balance. Hence, protecting endangered species is crucial not just for their survival, but for the preservation of biodiversity and the wellness of our planet.
Every effort made towards conservation helps in sustaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. It ensures that future generations inherit a world that is rich in natural beauty and ecological complexity. By safeguarding endangered species, we are, in essence, protecting the very fabric of life on Earth.